ตำรายาของประเทศไทย
Thai Pharmacopoeia
สำนักยาและวัตถุเสพติด กรมวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์ กระทรวงสาธารณสุข
Bureau of Drug and Narcotic, Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Public Health Herbal drugs are liable to contain pesticide residues which accumulate from agricultural practices, such as spraying, treatment of soils during cultivation and administration of fumigants during storage. Many herbal drug preparations of plant origin are taken over long periods of time; limits for residues should therefore be established.
Definition For the purposes of the Pharmacopoeia, a pesticide is any substance or mixture of substances intended for preventing, destroying or controlling any pest, unwanted species of plants or animals causing harm during or otherwise interfering with the production, processing, storage, transport or marketing of herbal drugs. The item includes substances intended for use as growth-regulators, defoliants or desiccants and any substance applied to crops either before or after harvest to protect the commodity from deterioration during storage and transport.
Limits Unless otherwise indicated in the monograph, the herbal drug being examined at least complies with the limits indicated in Table 1. (The calculation is based on 60 kg of body weight.) Limits for pesticides that are not listed in Table 1 are calculated using the formula:
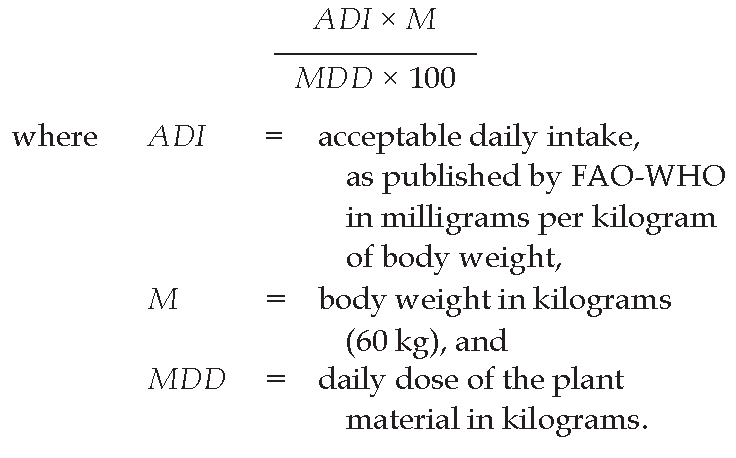
If the plant herbal drug is intended for the preparation of extracts, tinctures or other pharmaceutical forms the preparation method of which modifies the content of pesticides in the finished product, the limits are calculated using the following formula:
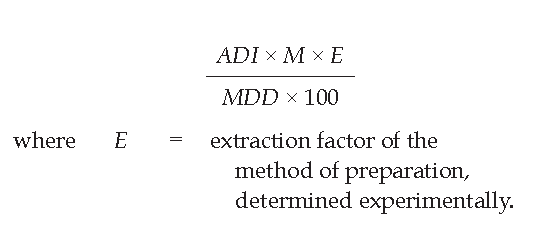
Higher limits can also be authorized, in exceptional cases, especially when a plant requires a particular cultivation method or has a metabolism or a structure that gives rise to a higher than normal content of pesticides. The competent authority may grant total or partial exemption of the test when the complete history (nature and quantity of the pesticides used, date of each treatment during cultivation and after the harvest) of the treatment of the batch is known and can be checked precisely.
Sampling
METHOD For containers up to 1 kg, take one sample from the total content, thoroughly mixed, sufficient for the tests. For containers between 1 and 5 kg, take three samples, equal in volume, from the upper, middle and lower parts of the container, each being sufficient to carry out the tests. Thoroughly mix the samples and take from the mixture an amount sufficient to carry out the tests. For containers of more than 5 kg, take three samples, each of at least 250 g from the upper, middle and lower parts of the container. Thoroughly mix the samples and take from the mixture an amount sufficient to carry out the tests.
SIZE OF SAMPLING If the number (n) of containers is three or fewer, take samples from each container as indicated above under Method. If the number of containers is more than three, take samples as indicated under Method, from √n + 1 containers,rounding up to the nearest unit if necessary.
The samples are to be analyzed immediately to avoid possible degradation of the residues. If this is not possible, the fresh samples should be stored in the refrigerator, but typically no longer than 5 days. Dried samples may be stored at room temperature, but if storage time is expected to exceed two weeks, they should be sub-sampled and stored in the freezer (–10°).


Qualitative and quantitative analysis of pesticide residues
Use either of the following analytical procedures:
— Analytical procedures issued by National Authorities or International Standard Organizations, or those published in internationally recognized manuals or publications;
— Analytical procedures with appropriate and reliable performance characteristics validated by a collaborative study or single-laboratory study according to the internationally recognized protocols. The validated analytical procedures shall be assessed in compliance with the latest version of ISO/IEC 17025. The analytical procedures stated above shall be capable of providing the reliable results of the specified maximum pesticide residue level.
In addition, they shall satisfy the following criteria:
— The chosen method, especially with respect to its purification steps, is suitable for the combination of pesticide residue and substance to be examined, and is not susceptible to interference from co-extractives;
— The limit of quantification for each pesticide matrix combination to be analyzed is not more than the corresponding tolerance limit; the method is shown to recover between 70 and 120 per cent of each pesticide with a repeatability not less than 20 per cent relative standard deviation. (Note The lower recoveries may be acceptable in certain cases.) The concentration of the test and standard solutions and the setting of the apparatus are such that a linear response is obtained from the analytical detector.
